CATALOGUE
DATA VISUALIZATION
Data visualization is a visual representation of information that is gained from data. It can take many shapes in charts, graphs or infographics. The opportunities are endless, only depends on creativity.
The goal of data visualization is to communicate, share information, tell a story to other people in a way that they can understand it.
Our brain is designed to decode visual information faster than written ones. This is why visualizing became popular. A good visualization doesn't need explanation.
There are many kinds of visualization that you can create from your data. The question is, how much time you want to spend with it. If not too much, you are in the right place.
With the Suggested Charts function in AnswerMiner, you can create beautiful visualizations by clicking on the data you want to represent. Also, there is a way to start from the other way by choosing the visualization type and then adding the values.
In this catalog, we collected the visualizations that you can create with AnswerMiner. Use this page as a navigation tool to find the best visualization that fits your imagination or just explore different chart types.
Area
The area chart or area graph is used to display quantitative data. Use it when comparing one to another or more quantities. It is also beneficial for showing trends. Use colors to differentiate variables.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Height (Y-axis)
X-axis
Coloring
Tooltip
Bar
The bar chart is one of the most often used visualizations. It is used to show changes over time or to compare different categories and part-whole connections. The bars are placed vertically and differentiated by colors.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Width
Stack
Coloring
Tooltip
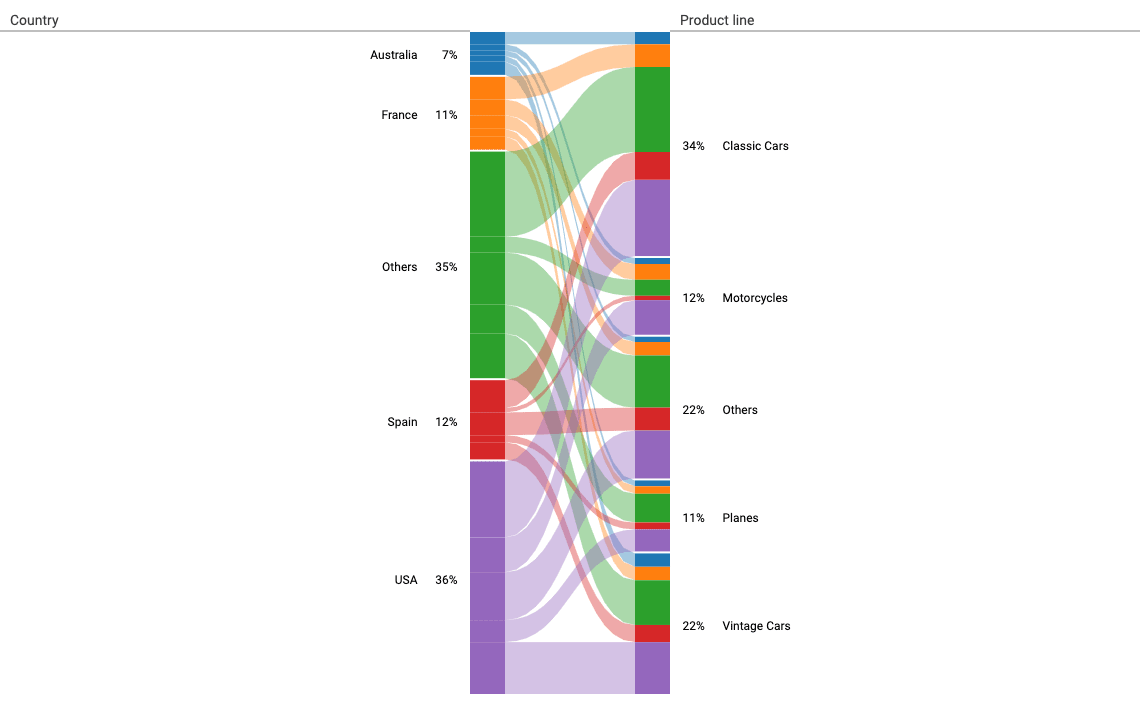
BiPartite
The BiPartite chart is used to show a connection between two categorical variables (columns). With this chart, subsegments can be easily examined. It is a very popular chart among AnswerMiner users.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Left and Right values
Box Plot
The Box Plot is a tool in descriptive statistics that can help you to get a clearer picture of the distribution and the most important values or outliers in your dataset at the same time.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Size
Stack
Fill color
Whiskers mode
Tooltip
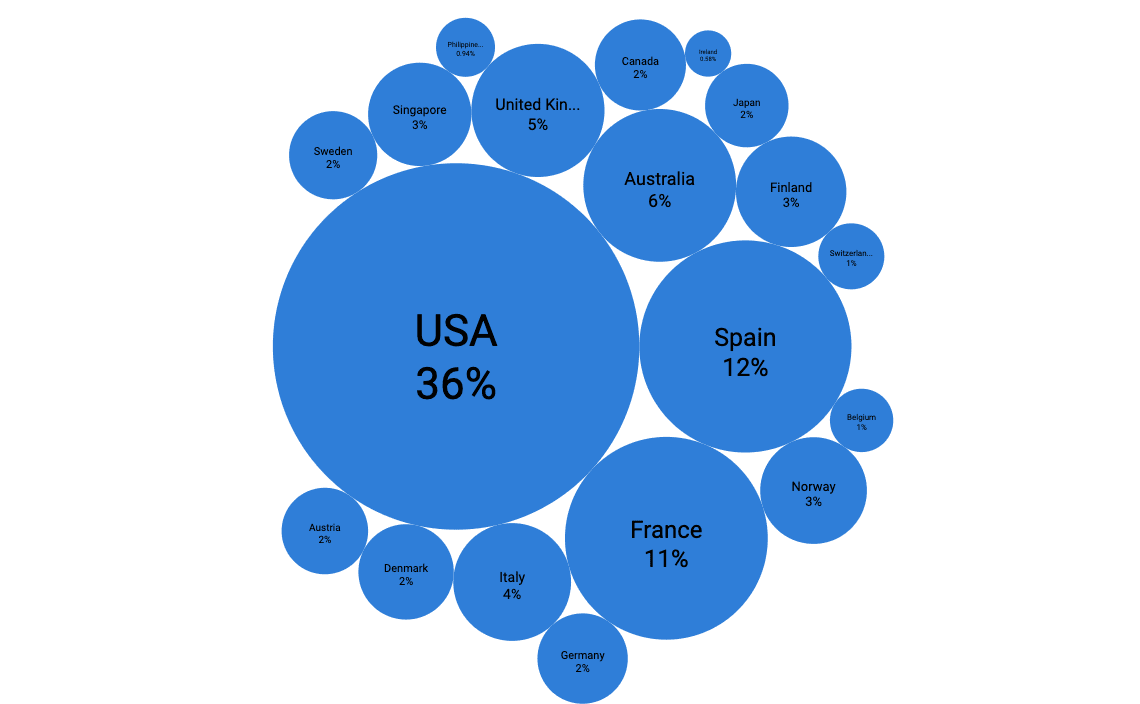
Bubble Cloud
The Bubble Cloud a great tool to show the distribution of categorical values and also add more dimensions by using size and color.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Bubble separation
Size of bubbles
Coloring
Tooltip
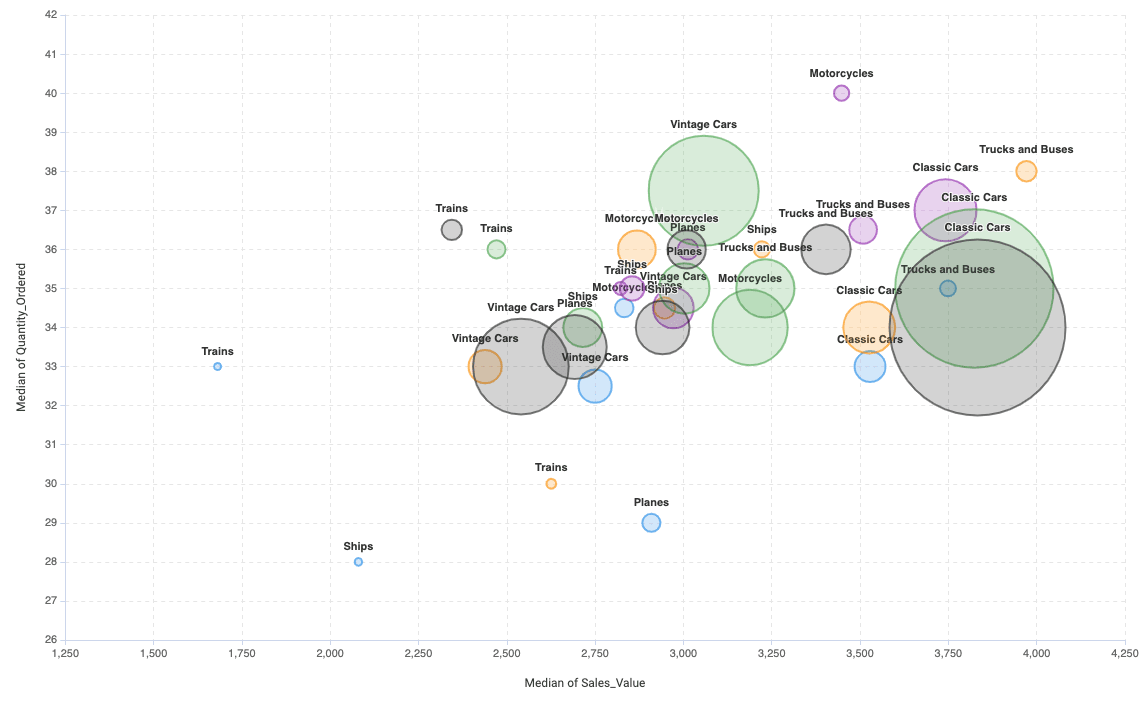
Bubble Plot
The Bubble Plot is a complex chart that is a scatter plot with more dimensions: separations, size, and color. It is used to visualize numerical values that are segmented by different categories.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
X-axis position
Y-axis position
Bubble separation
Size of the bubbles
Coloring
Tooltip
Bullet chart
The Bullet chart is a variation of the bar chart. It is used to compare one or more measures and highlight target numbers like KPIs.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Target value
Stop1
Stop2
Stop3
Stop4
Column chart
The Column chart is very similar to bar chart. It is also used to show distributions, but instead of horizontal bars it uses standing, vertical columns. It can improve with coloring dimensions.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Height
Stack
Coloring
Tooltip
Cross tab
The Cross tab is a table where two or more variables are cross-tabulated. It can be a great representation of information with limited columns and rows, otherwise it can be difficult to understand.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Rows
Columns
Value
Donut chart
The Donut chart is an alternative to the Pie chart. It shows the same information with a bit change of the design.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Angle
Sliced by
Coloring
Tooltip
Gauge chart
The Gauge chart is or also called speedometer is to show a single value. It can be numerical or categorical value. For numerical values, some kind of aggregations (mean, median, sum) is used. For categorical data, a chance is displayed in percentage.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Data to display
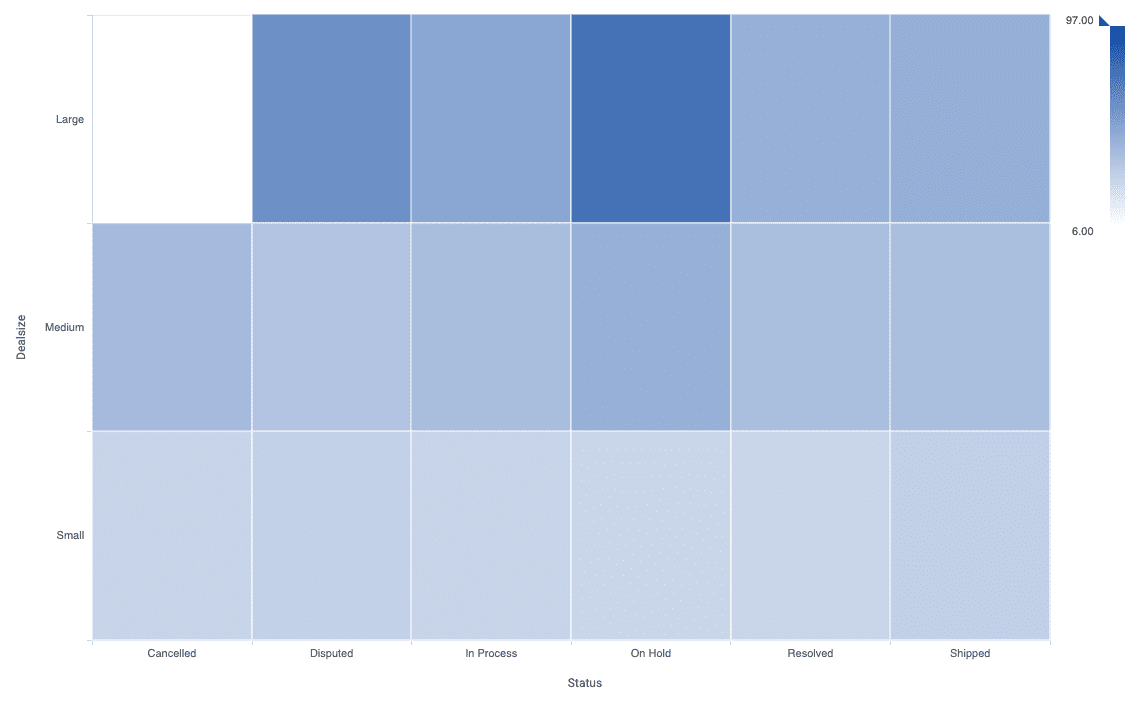
Heatmap
The Heatmap is a data visualization technique that helps to discover focus points and groups in data by using color in two dimensions. The strength of the color shows where the data point are grouped. By default the darker the data the higher the density is.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Columns
Rows
Cell color
Tooltip
Histogram
Histograms are column-shaped charts, in which each column represents a range of the values, and the height of a column corresponds to how many values are in that range. Select a numerical column in your dataset and AnswerMiner will create the Histogram automatically.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Stack: Select a numerical or an ordinal value
KPI chart
The KPI chart is as simple as it names said. It shows one numerical value, which is mostly a KPI. Sometimes one number tels more than any visualization.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Data to display
Line chart
The Line chart is one of the most popular chart types. It is a great graph to visualize time series. On the X-axis can be showed the time from left to right and the Y-axis shows the values. Use it to show trends, changes, or seasonality by time.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Height
X-axis
Separation
Coloring
Tooltip
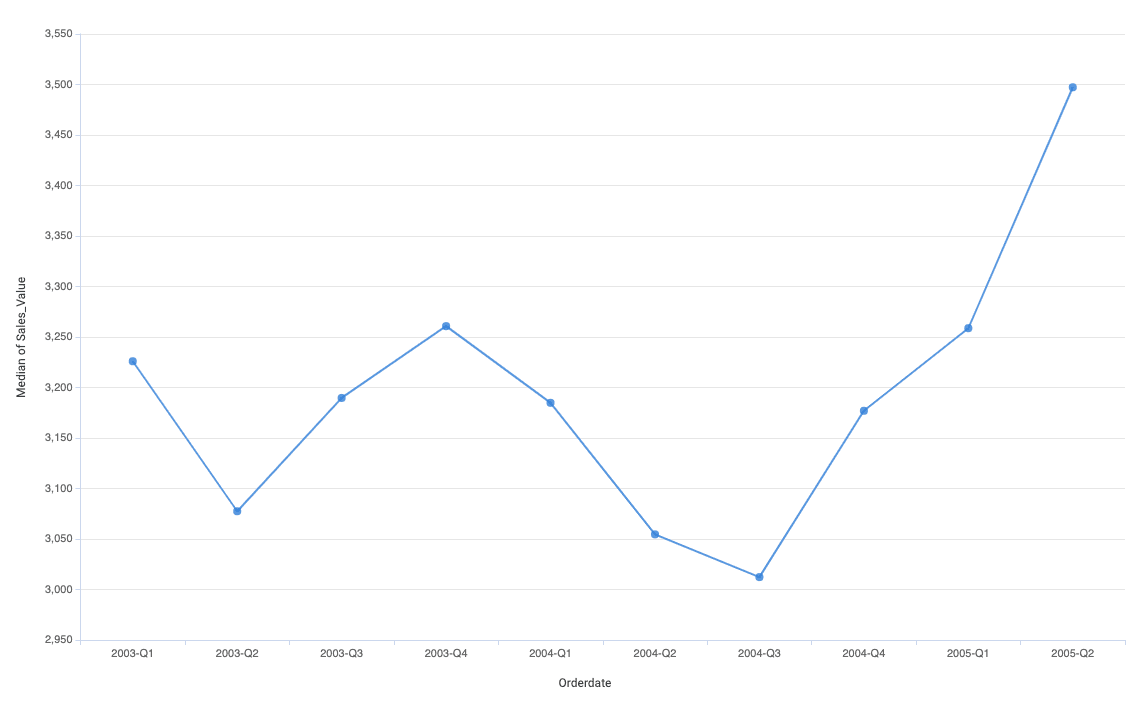
Line range chart
The Line Range chart shows almost the same information as the line chart, but it also shows the low and top 25% that helps to understand the meaning of the chart.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Height
X-axis
Separation
Coloring
Tootlip
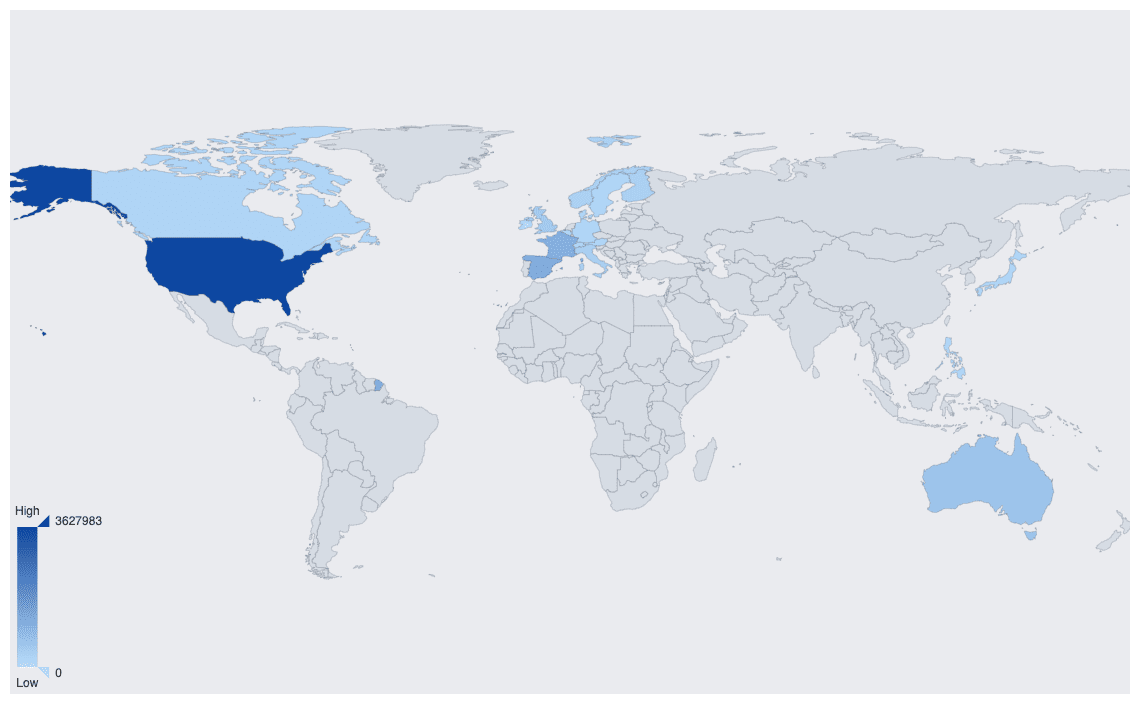
Map chart
The Map chart shows country, city, or any kind of geographically related aggregations on a map.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Country
Coloring
Map
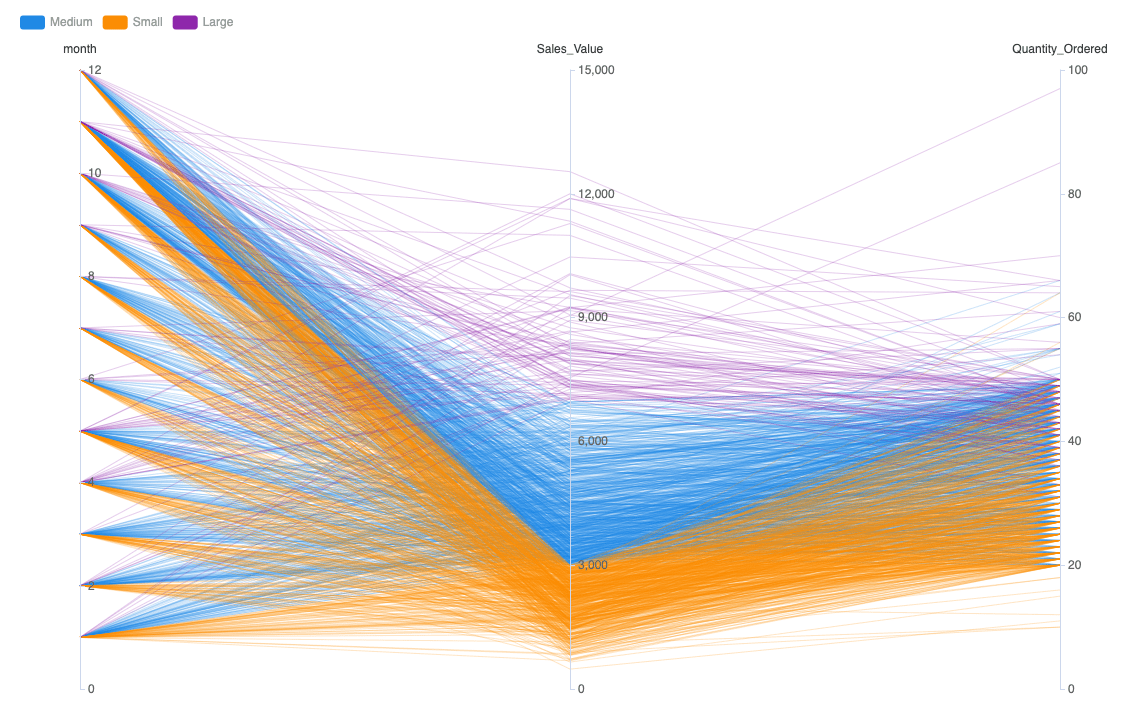
Parallel Coordinates
In parallel coordinates plot or simply parallel coordinates, each quantitative variable is represented by an equally spaced vertical line. All the other lines that connect axes are separate values. The scaling of the axes can be different as each variable has its own measurement unit or it can be normalized to keep the uniformity.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Columns
Coloring
Pie chart
The Pie chart is one of the most used and misused distribution charts. That shows the distribution of the given data with the size of a “slice”.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Angle
Sliced by
Coloring
Tooltip
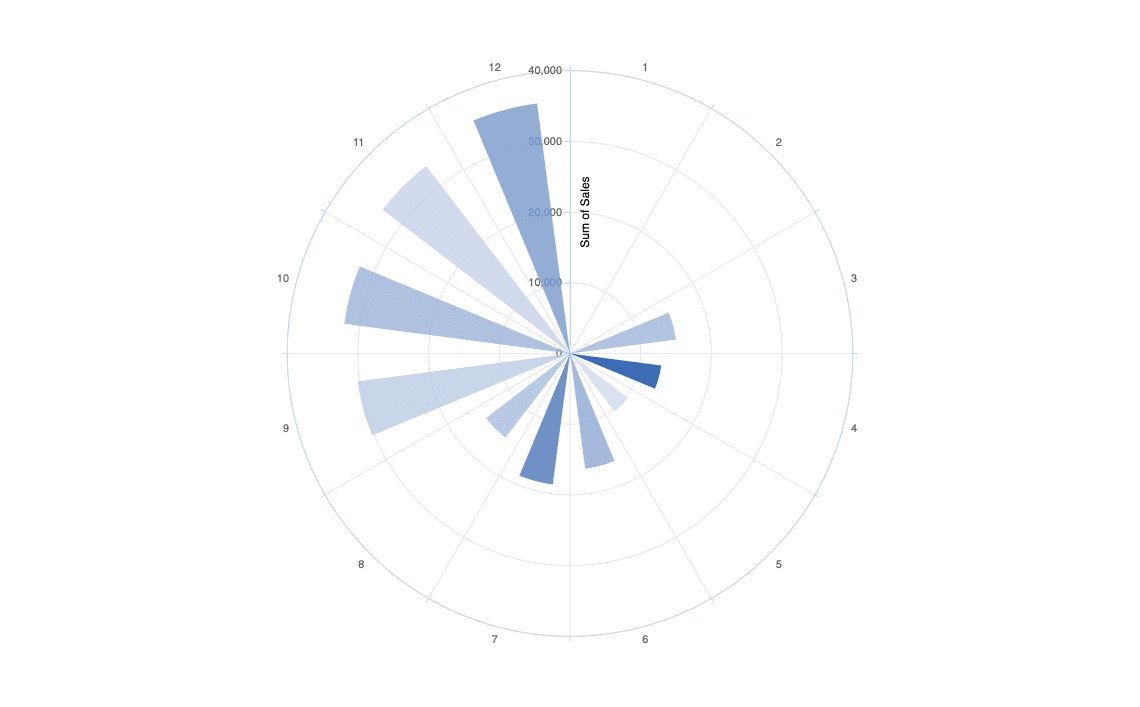
Polar bar chart
The Polar bar chart is a visualization for date-time and numerical data. It works the best for monthly, daily or hourly representation of numerical data like sales value, ordered quantity, or other financial data.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Size
Stack
Coloring
Tooltip
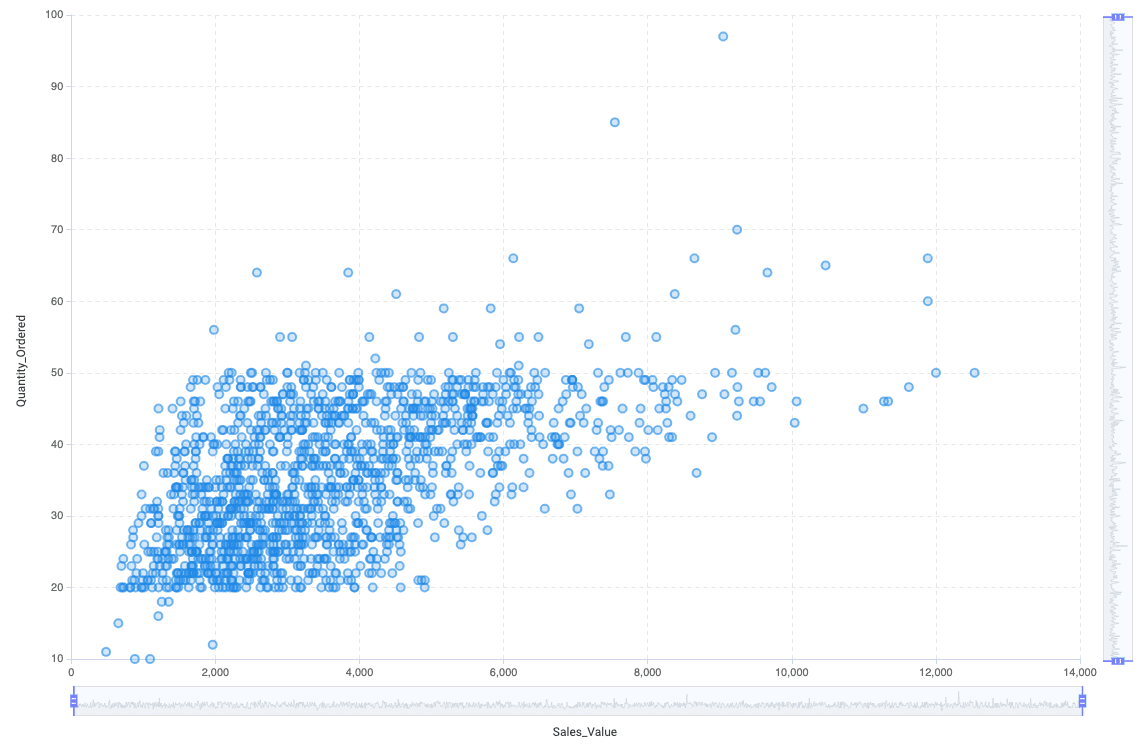
Scatter Plot
The Scatter Plot is perfect to show the correlation between two numerical variables and also show trends. All data points are placed in a two-dimensional coordinate system.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
X-axis position
Y-axis position
Coloring
Tooltip
Summary chart
The Summary chart contains all the important statistical information about the selected column, Range, Average, Median, Standard deviation, and so on.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Data to display:
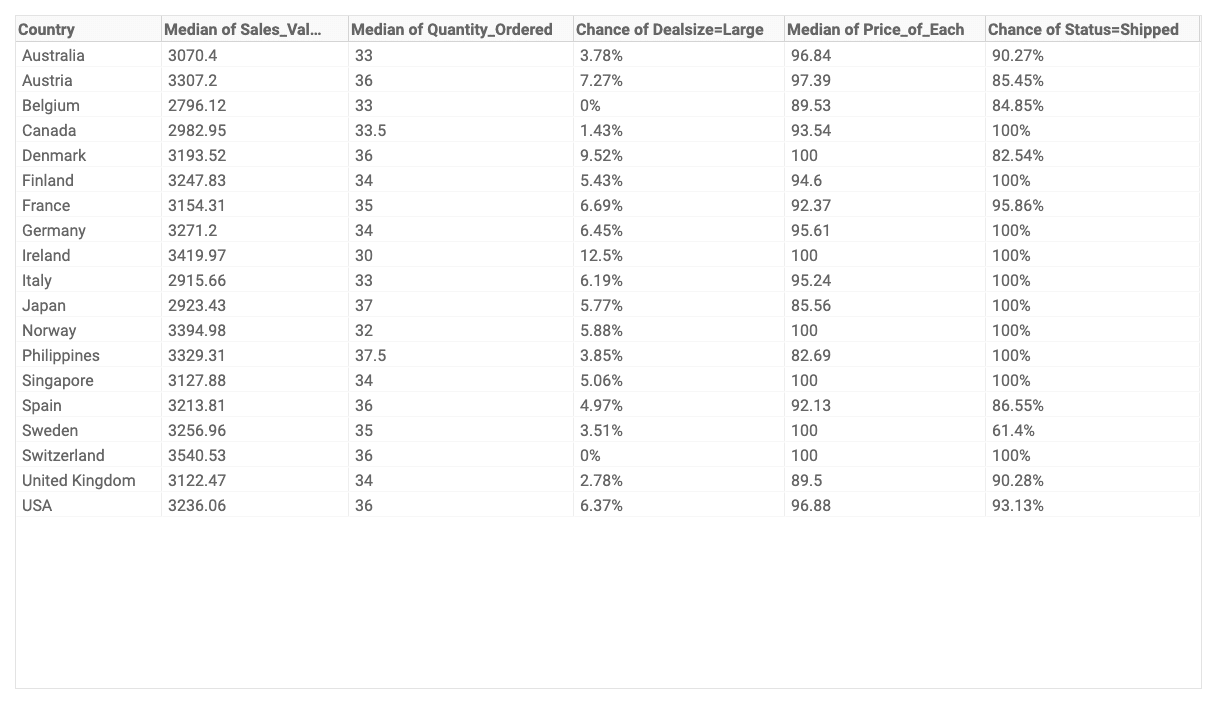
Table chart
The table chart is a table where you can create a new aggregate table from the original dataset. First, select a categorical variable to display in rows and then add columns. When adding a column you can select from different aggregations.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Rows
Columns
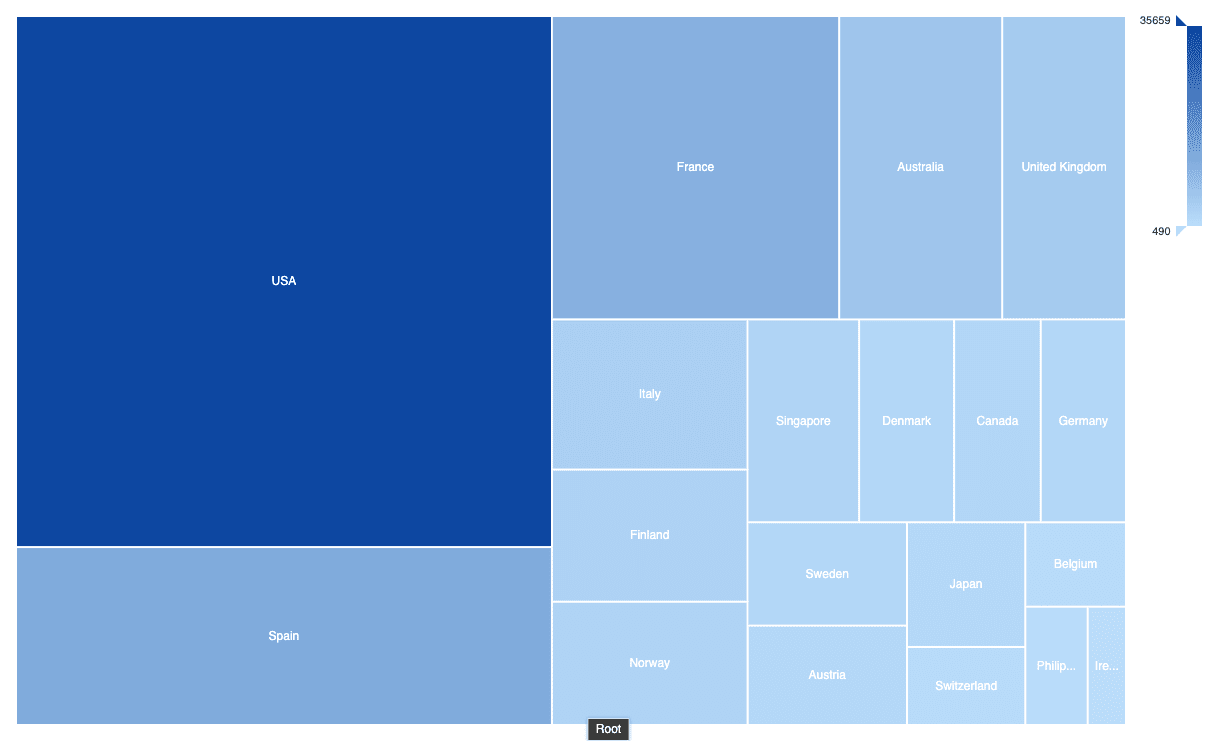
TreeMap
The TreeMap is a tool to display distribution with area size. Coloring can be used as an additional dimension.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Size of rectangles
Separation by
Coloring
Tooltip
Word Cloud
The Work Cloud is a very good way to highlight a specific category or value. This chart is less informative than other visualizations but looks very good on a dashboard or infographic.
Parameters in AnswerMiner
Words
Size of words
Coloring

