Box Plot is a tool in descriptive statistics that can help you to get a clearer picture of the distribution and the most important values or outliers in your dataset at the same time.
This method was first introduced for a wider audience in 1969 by John W. Tukey, who used boxes and so-called whiskers to visualize distribution and variability in data.
Box Plots also allow the quick investigation of one or more datasets. They may seem simple at first sight, but the space they take compared to a histogram and the possibility to compare several groups of data makes it a well-utilizable tool during the analytical process.
What Box Plot Tells
Box Plot is a graphic method to depict the five number summary of your given dataset.
- The minimum is the lowest point of your data, excluding any possible outliers.
- The first quartile or lower quartile (Q1) is the median of the lower half of your dataset.
- Median is the middle value of your dataset. (Do not mix it with mean.)
- The third quartile or upper quartile (Q3) is the median of the upper half of your dataset.
- Maximum is the largest point of your data, excluding any possible outliers.
The interquartile range or IQR that represents the distance between the upper and lower quartiles is pictured as a box.
How Box Plot Work
When a box plot is created, the box is drawn between the first and the third quartile, and a horizontal line within the box pictures the median. If there are any outliers in data, they are shown as circle, star, or X sing.
Whiskers can be also applied to connect the minimum and maximum values to the box-shaped part of the graph. Hence the name box and whisker plot, as Tukey originally used whiskers to indicate even the symmetry and normality in distribution with them.
Box plots divide your data into four sections that contain approximately 25 percent of the data in that set. Under normal distribution, this will be exactly 25% and symmetric, but in most cases the ratio and the size of the quartiles are different.
The spread of data can be easily detected by looking at the minimum or maximum values at the end of the whiskers.
Skewness can be also measured by using box plot. If you look on the chart and see the difference in the placement of the median within the box, while the whiskers are shorter or longer in the direction of extreme values, it shows positive or negative skew.
How Box Plot Identifies Outliers
An outlier is a particular data that is numerically far from the rest of the set.
Defining outliers in data with graphical methods is possible, but the outcome is not always easily interpretable. If you are using, for example a Gaussian curve, you will not be able to see the extremity of these values.
However, box plots are created to visualize the outliers. This can be seen in the form of small marks outside of the whiskers.
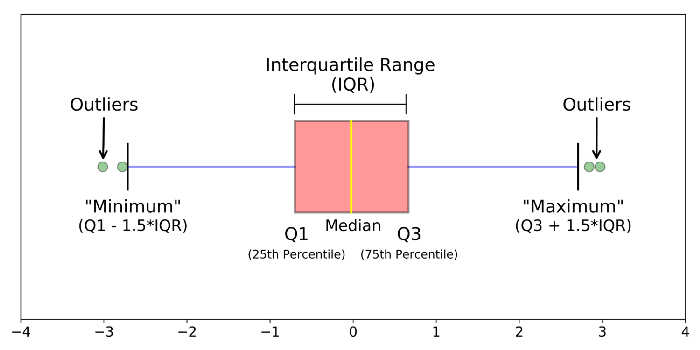
In this example, outliers can be found outside 1.5 times the interquartile range below the lower quartile and above the upper quartile (Q1 - 1.5 * IQR or Q3 + 1.5 * IQR).
Box Plot in Statistics
Since its first appearance, box blot is favored by researchers due to the insights they get from it and the space it spares. Different variations of box plot evolved throughout the years that indicate more and help to recognize the differences between datasets. The two most common variations are variable width and notched box plot.
Variable width box plot pictures the size of each plotted data group by making the width of the box proportional to the square root of the size of the group.
Notched box plot is narrower around the median. The width of the notch is proportional to the IQR of the sample and inversely proportional to the square root of the size of the sample.
Notched boxes can also indicate the statistically significant difference between the medians. If two notches do not overlap, that is a clear sign of it.
Now, let us have a closer look at the creation of box plots by using the data visualisation platform AnswerMiner.
How to Create Box Plot with AnswerMiner
In order to create a box plot, you have to open your dataset in AnswerMiner first. If you don’t have one, use our sample sets.
Pick your variables, using the Suggested Charts feature so based on that data AnswerMiner smart algorithm will make the box plot visualization. The other way is to create a box plot straight by clicking on the Create Chart button on the left sidebar.
After clicking on the Box Plot icon, you can set up your chart. In this example, we are using the SalesOrderTable sample dataset to visualize the differences between countries.
Choose the Sales_value as Size and Country as Stack values.
The visualization is almost complete, only the color is missing. In this case, we use the median of Priceofeach for colorization. The results are as follows.
Sales Value by Country Colored by Price of Each Product
Summary
Box plot, or box and whisker plot is an important graphic visualization method to oversee and compare multiple data groups at the same time. It can also be used to detect outliers in data at an early stage.
Spread and skewness of data can be shown by the different placement and size of the box and of the whiskers.
Most importantly, box plots describe and summarize the five core values of the given set of data in an easy to understand way.

